BREAST AUGMENTATION
Dr Tan Ying Chien | Dr Chia Hui Ling
Breast augmentation is a plastic surgery procedure that involves the insertion of breast implants into the breast to enhance its size and shape.
A woman may consider breast augmentation for the following reasons:
- She wants to increase the size of her breasts
- Her breasts have lost shape and volume following pregnancy, breastfeeding or massive weight loss
- She wishes to balance her breasts which are unequal in size
Although undergoing breast augmentation is a personal choice, it is advised to discuss it with someone close to you. It will not be wise to undergo this procedure to please someone else, and you should make this decision based on your own needs. Speaking to someone who had undergone a breast augmentation procedure may help you to understand the process better.
TREATMENT
Have a thorough discussion with your plastic surgeon, informing him / her your surgical goals, medical conditions, drug allergies, medications and previous surgeries.
These are important aspects of breast augmentation that should be raised during your consultation with your plastic surgeon:
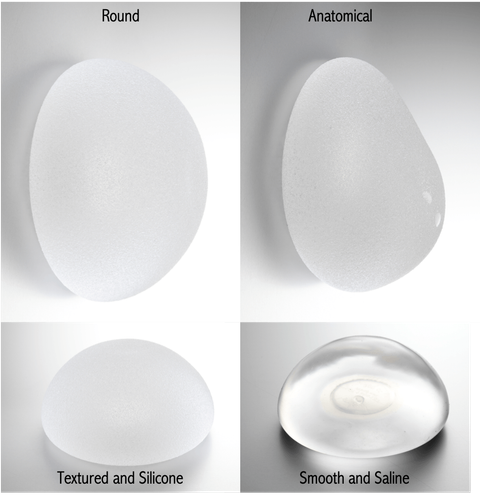
1. Types of Implants
- Implant shape: Round v Anatomical (Tear Drop)- Implant surface: Smooth v Textured
- Implant content: Silicone v Saline

2. Location of the Scars
- Inframammary (crease below the breast)
- Axillary (armpit)
- Periareolar (around the areola)
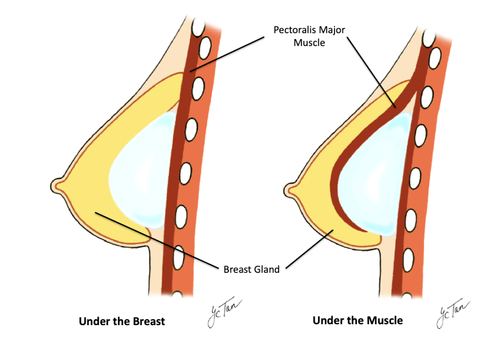
3. The Placement of Implants
- Subglandular (Above the pectoralis and under the breast)
- Subpectoral (Under the pectoralis muscle)
4. Additional procedures
The details of the procedure, expected outcomes, risks and other treatment options (eg, fat transfer or hybrid breast augmentation) should also be explained to you.
Your surgeon may use a 3D-imaging simulation system to help you visualise the possible result after breast augmentation. Or you may be asked to wear a tight T-shirt, and implants of different sizes are inserted under the T-shirt to simulate the augmentation.
COMPLICATIONS AND MANAGEMENT
Risks of Breast Augmentation include:
- Anaesthetic risks
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Implant leak
- Capsular contracture (hardening)
- Unsatisfactory implant position and size
- Visible implant rippling
- Asymmetrical results
- Altered nipple sensation
- Poor scarring
- BIA-ALCL*
In the event of a complication, your surgeon may advise a revision surgery. In the case of early capsular contracture, the surgeon may prescribe a medication to curb its progress.
*BIA-ALCL
An uncommon complication with the use of textured implant is Breast Implant Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, or BIA-ALCL. The risk ranges from 1 in 30,000 cases to 1 in 4000 cases. There are currently no known reported cases occurring in Oriental patients in the medical literature. Do contact your plastic surgeon if you experience breast enlargement at 1 year or more after your surgery (most common sign), or if you develop a mass in your breast or axilla.
